why still watch fake news Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. 😞 Kekurangan Nomor Seri Louis Vuitton: Adanya kemungkinan nomor seri palsu; Keterbatasan informasi yang diberikan nomor seri; Cara Cek Nomor Seri Louis Vuitton. Langkah pertama dalam memeriksa nomor seri Louis Vuitton adalah mengetahui posisi nomor seri pada tas atau barang yang Anda miliki.
0 · Why we fall for fake news: Hijacked thinking or laziness?
1 · Why we believe fake news
2 · Why is fake news so prevalent? Researchers offer some answers
3 · Why do people around the world share fake news? New research
4 · Why Are We Still Falling for Fake News?
5 · What can be done to reduce the spread of fake news? MIT Sloan
6 · Fake news: What it is, and how to spot it
7 · Fake news study: Most Americans can’t spot fake news, study finds
8 · A main reason people share fake news: Lack of attention, study
9 · 7 Reasons Why We Fall for Fake News
Biroja apgaismojums. Biroja apgaismojums. Griestu Galda Spotlampas. Galda lampa DUCHESSA TL1 SMALL Transparent. Āra apgaismojums. Āra apgaismojums. Sienas griestu Piekaramās . Brīvības iela 105, Rīga, LV-1002, Latvija Klientu serviss: [email protected] Facebook; Youtube; Instagram; Kontakti. Visas cenas norādītas .
Why Are We Still Falling for Fake News? Study finds that humans believe what they see. Posted May 29, 2019 | Reviewed by Davia Sills. Fake News. Source: Pixabay. “Believe nothing you hear, and. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation “The dominant explanation for why people believe fake news has been that their reasoning is held captive by partisan biases—their thinking gets hijacked,” Rand says. His studies paint an alternate picture: “People who believe false things are the people that just don’t think carefully,” he says.
By analyzing survey results from over 500 participants, they found that when fake news headlines are repeated, people are more likely to believe them even if they don’t align with the.
Why we fall for fake news: Hijacked thinking or laziness?
Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. Psychology. Why we believe fake news. (Image credit: Getty Images) By Tom Chatfield 9th September 2019. The pace of life in the 21st Century has created “infostorms” that overwhelm our.
1. Confirmation bias. Confirmation bias refers to our favoring of information that confirms our existing beliefs. Without accounting for this bias in our thinking, we are more likely to fall. Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health. CNN — As many as three in four Americans overestimate their ability to spot false headlines – and the worse they are at it, the more likely they are to share fake news, researchers reported.
The research team’s findings have implications for how social media companies can stem the flow of misinformation. Platforms could, for instance, implement simple accuracy prompts to shift users’ attention towards the reliability . Why Are We Still Falling for Fake News? Study finds that humans believe what they see. Posted May 29, 2019 | Reviewed by Davia Sills. Fake News. Source: Pixabay. “Believe nothing you hear, and. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation
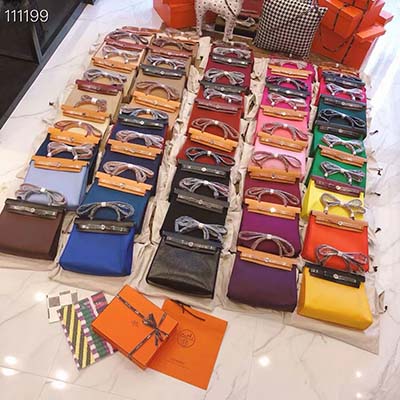
gucci bag with horseshoe
“The dominant explanation for why people believe fake news has been that their reasoning is held captive by partisan biases—their thinking gets hijacked,” Rand says. His studies paint an alternate picture: “People who believe false things are the people that just don’t think carefully,” he says. By analyzing survey results from over 500 participants, they found that when fake news headlines are repeated, people are more likely to believe them even if they don’t align with the.
Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. Psychology. Why we believe fake news. (Image credit: Getty Images) By Tom Chatfield 9th September 2019. The pace of life in the 21st Century has created “infostorms” that overwhelm our.
1. Confirmation bias. Confirmation bias refers to our favoring of information that confirms our existing beliefs. Without accounting for this bias in our thinking, we are more likely to fall. Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health. CNN — As many as three in four Americans overestimate their ability to spot false headlines – and the worse they are at it, the more likely they are to share fake news, researchers reported.
The research team’s findings have implications for how social media companies can stem the flow of misinformation. Platforms could, for instance, implement simple accuracy prompts to shift users’ attention towards the reliability . Why Are We Still Falling for Fake News? Study finds that humans believe what they see. Posted May 29, 2019 | Reviewed by Davia Sills. Fake News. Source: Pixabay. “Believe nothing you hear, and. Since the 2016 U.S. Presidential election and British “Brexit” referendum — and then COVID-19 — opened the floodgates on fake news, research has delved into the psychology behind online misinformation “The dominant explanation for why people believe fake news has been that their reasoning is held captive by partisan biases—their thinking gets hijacked,” Rand says. His studies paint an alternate picture: “People who believe false things are the people that just don’t think carefully,” he says.
By analyzing survey results from over 500 participants, they found that when fake news headlines are repeated, people are more likely to believe them even if they don’t align with the. Many Americans share fake news on social media because they’re simply not paying attention to whether the content is accurate — not necessarily because they can’t tell real from made-up news, a new study in Nature suggests. Psychology. Why we believe fake news. (Image credit: Getty Images) By Tom Chatfield 9th September 2019. The pace of life in the 21st Century has created “infostorms” that overwhelm our.
1. Confirmation bias. Confirmation bias refers to our favoring of information that confirms our existing beliefs. Without accounting for this bias in our thinking, we are more likely to fall. Fake news continues to proliferate - but how much do you know about separating fact from opinion, or truth from hoax? Online misinformation is slippery to define - but it has huge implications for everything from politics to health. CNN — As many as three in four Americans overestimate their ability to spot false headlines – and the worse they are at it, the more likely they are to share fake news, researchers reported.
does billie eilish need glasses
Why we believe fake news
Why is fake news so prevalent? Researchers offer some answers
nordstrom rack gucci bag
Caesars Palace is a luxury hotel and casino in Paradise, Nevada, United States. The hotel is situated on the west side of the Las Vegas Strip between Bellagio and The Mirage. It is one of Las Vegas's largest and best known landmarks. [1] [2]
why still watch fake news|Fake news study: Most Americans can’t spot fake news, study finds